|
Alexander (Sasha) Sax I am a senior research scientist at Meta Superintelligence Labs.
During my PhD, at UC Berkeley, I was advised by Jitendra Malik and Amir Zamir. In the summer of 2022, I interned at FAIR with Georgia Gkioxari. I got my MS and BS from Stanford University, where I was advised by Silvio Savarese and graduated with an Erdős number of 3. |

|
ResearchSome nice honors:
A few papers are highlighted. Equal contribution is indicated by * and listed in alphabetical order. |

|
SAM 3D: 3Dfy Anything in Images
Model tech lead (training paradigm, layout model) Meta Superintelligence Labs arXiv, 2025 project page / demo / paper / github A 1.8B flow matching model (6T training tokens) for single-image 3D generation, that predicts complete shape, pose, and texture for masked objects. Drove adoption of LLM training paradigm (pretraining→midtraining→SFT→DPO) and preference-based data engine (online DPO → reward models → rejection sampling). Designed and built layout model end-to-end (flow matching for pose, multimodal conditioning). 5:1 win rate over SOTA. |
|
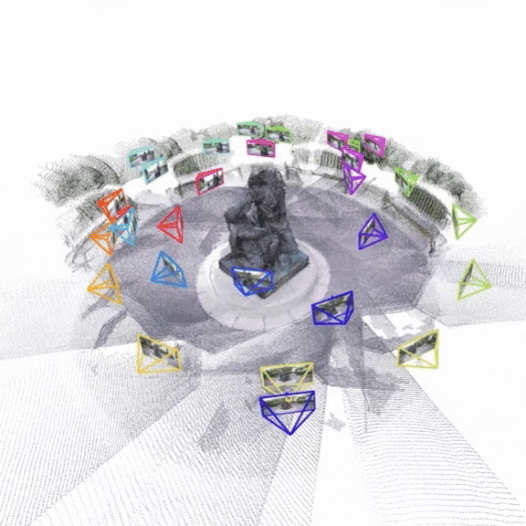
Fast3R: Towards 3D Reconstruction of 1000+ Images in One Forward Pass
Jianing Yang, Alexander Sax, Kevin J. Liang, Mikael Henaff, Hao Tang, Ang Cao, Joyce Chai, Franziska Meier, Matt Feiszli CVPR, 2025 project page / demo / paper / github Bitter lesson for SfM: replace the entire structure-from-motion pipeline with a single transformer. |

|
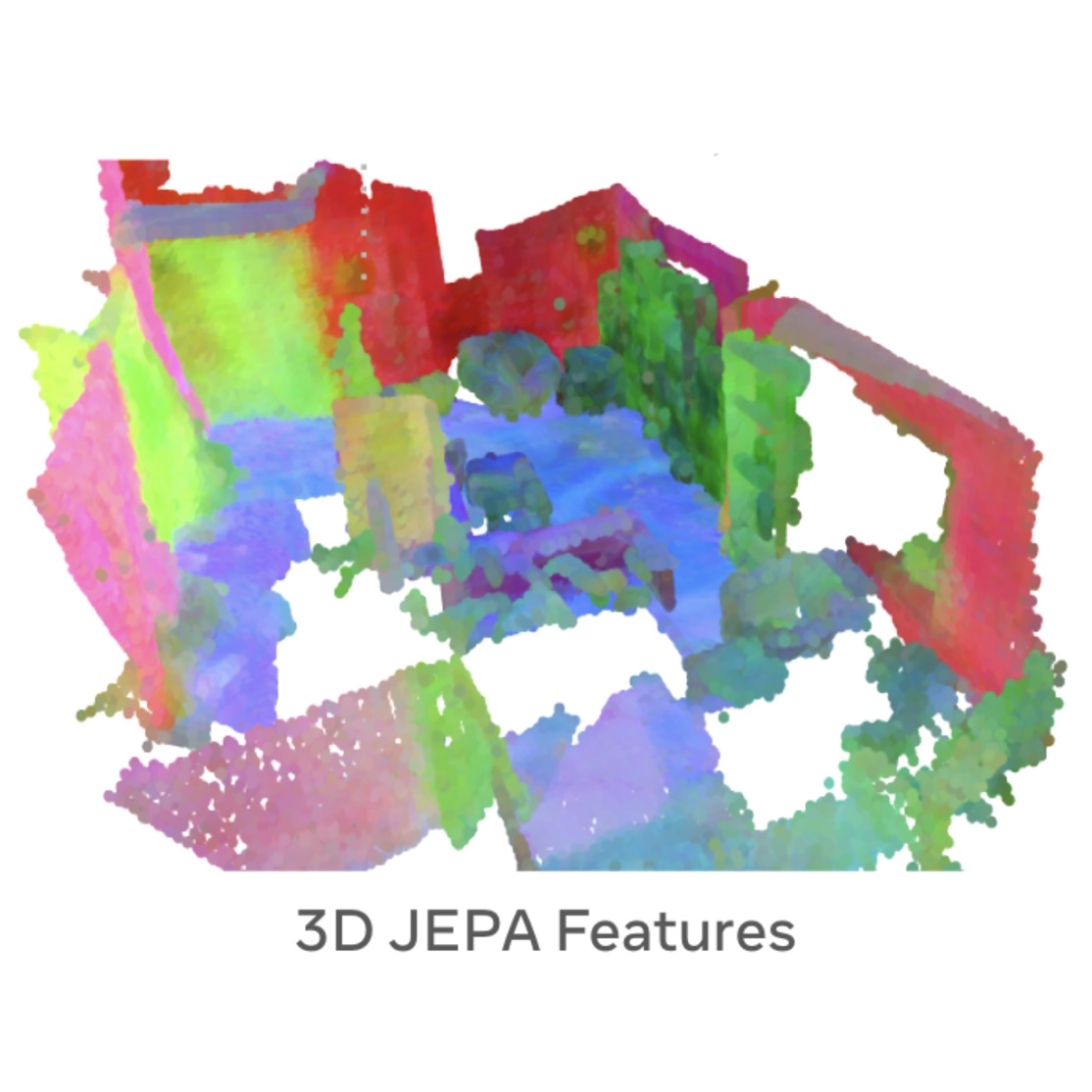
From Thousands to Billions: 3D Visual Language Grounding via Render-Supervised Distillation from 2D VLMs
Ang Cao, Sergio Arnaud, Oleksandr Maksymets, Jianing Yang, Ayush Jain, Sriram Yenamandra, Ada Martin, Vincent-Pierre Berges, Paul McVay, Ruslan Partsey, Aravind Rajeswaran, Franziska Meier, Justin Johnson, Jeong Joon Park, Alexander Sax ICML, 2025 project page / arXiv 3D vision-language grounding via distillation from 2D VLMs. Scaling behavior matches transfer learning predictions, achieving SOTA. Proposed render-supervised distillation approach; co-developed on design + implementation. |
|
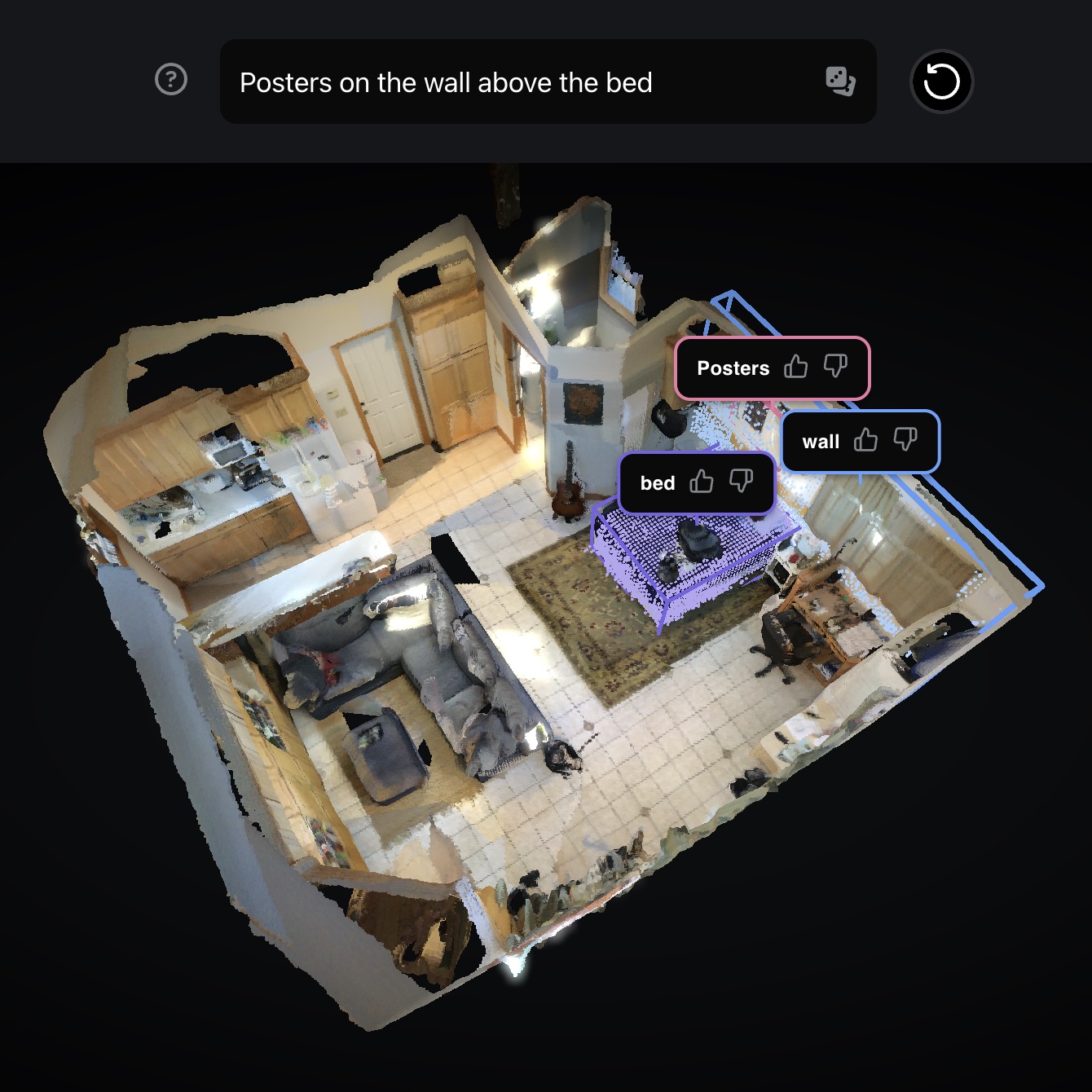
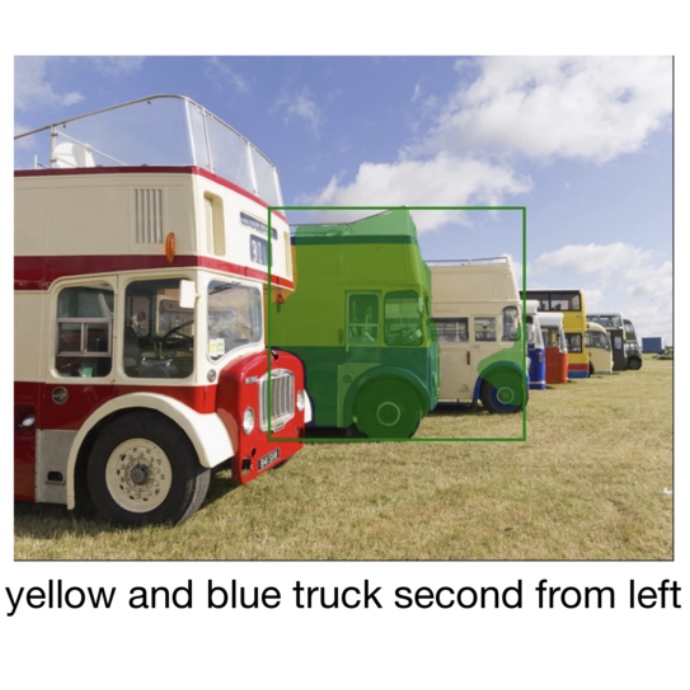
Locate 3D: Real-World Object Localization via Self-Supervised Learning in 3D
Tech lead (problem framing, evaluation design, training pipeline) Meta FAIR ICML, 2025 (Spotlight) website / demo / paper / github / model Language-based 3D localization in real-world scenes. Introduced problem framing; championed pre/post-training approach and proposed 2D annotation for data engine. Designed and built evaluations; led mask decoder development; drove dataset curation at 20-40x typical scale. |
 
|
UniVLG: Unifying 2D and 3D Vision-Language Understanding
Ayush Jain*, Alexander Swerdlow*, Yuzhou Wang, Sergio Arnaud, Ada Martin, Alexander Sax, Franziska Meier, Katerina Fragkiadaki ICML, 2025 project page / arXiv / github A unified transformer architecture that transfers between 2D and 3D with shared representations. SOTA performance in 3D language grounding benchmarks. |

|
OpenEQA: Embodied Question Answering in the Era of Foundation Models
The Cortex Team @ FAIR CVPR, 2024 project page / blog post / paper / github An open-vocabulary benchmark for Embodied Question Answering across 180+ real-world scenes. Humans far outperform VLMs on tasks that require complex spatial understanding. |
|
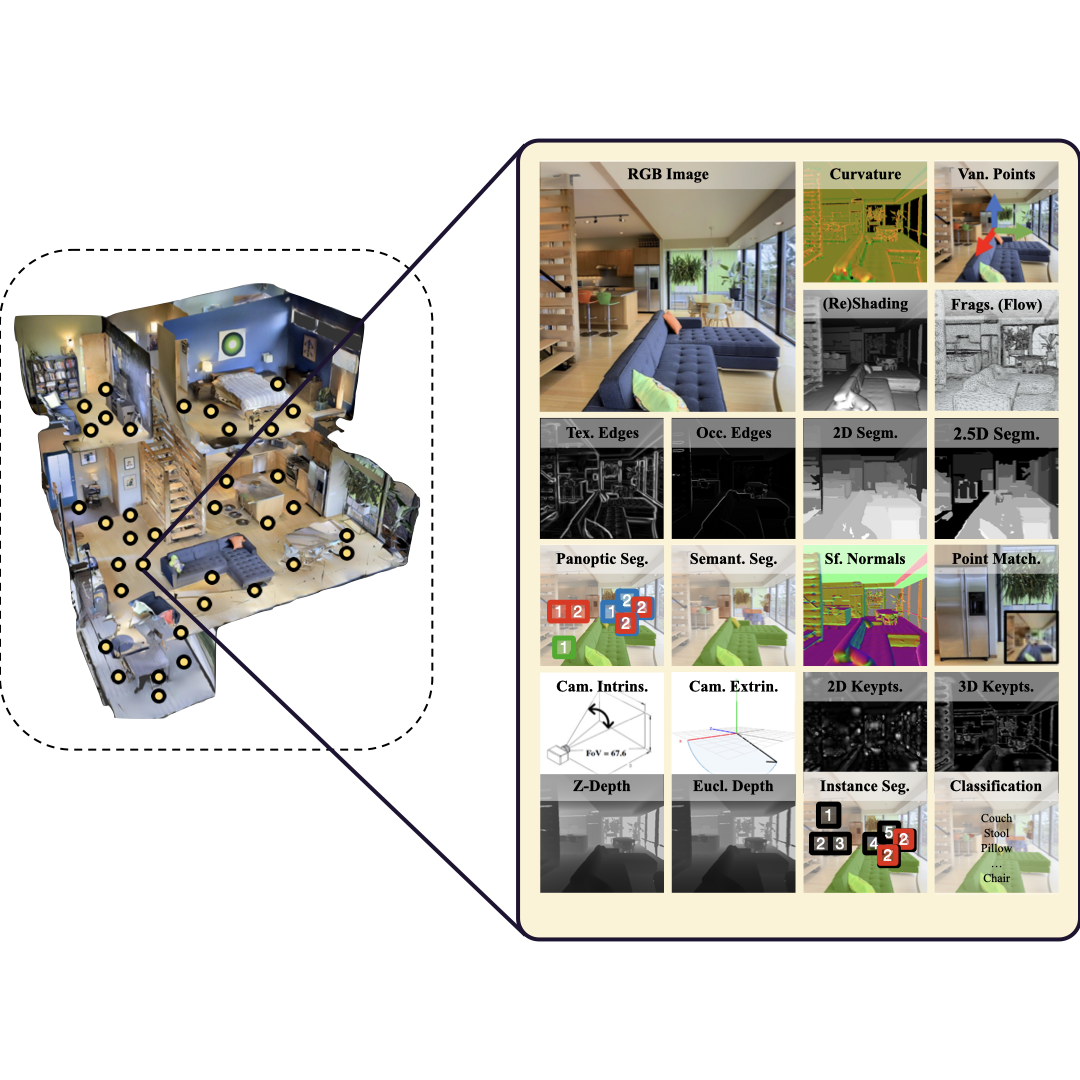
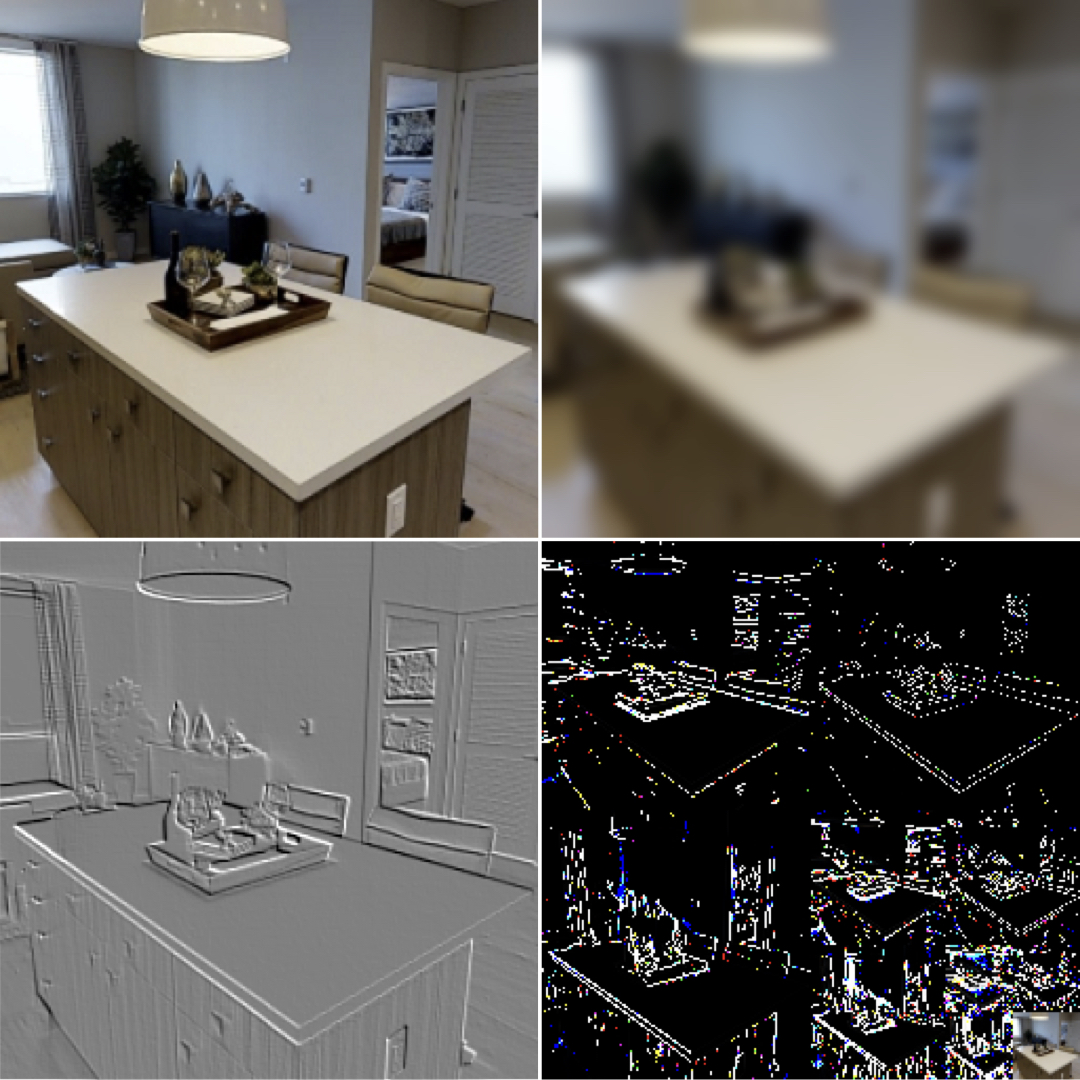
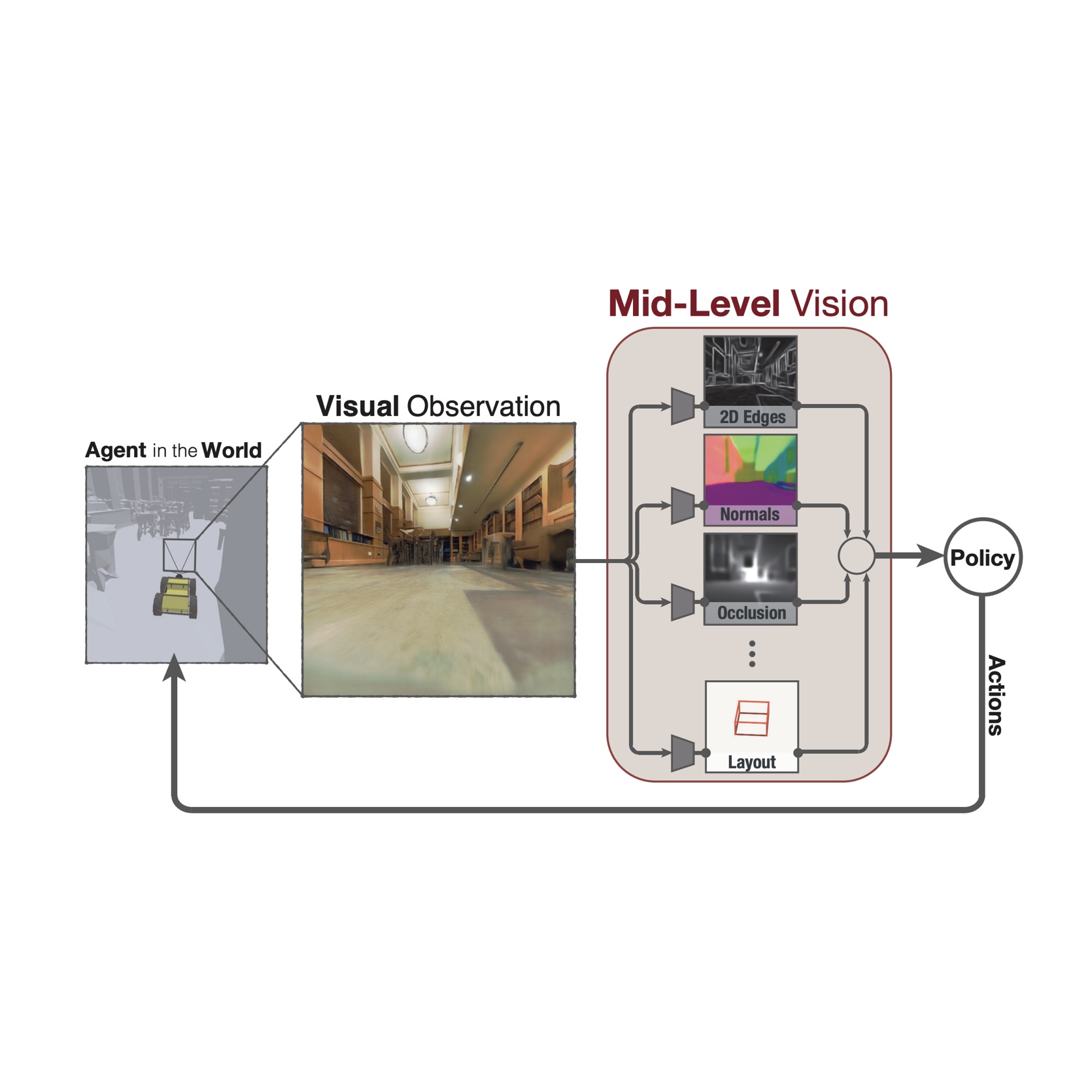
Omnidata: A Scalable Pipeline for Making Multi-Task Mid-Level Vision Datasets from 3D Scans
Ainaz Eftekhar*, Alexander Sax*, Roman Bachmann, Jitendra Malik, Amir Zamir ICCV, 2021 project page / arXiv / github A multimodal 2D/3D dataset of millions of frames from thousands of scanned and synthetic scenes. For surface normal estimation, ViTs trained on Omnidata achieve human-level performance on OASIS. SOTA depth and the annotation engine is released as OSS. |
|
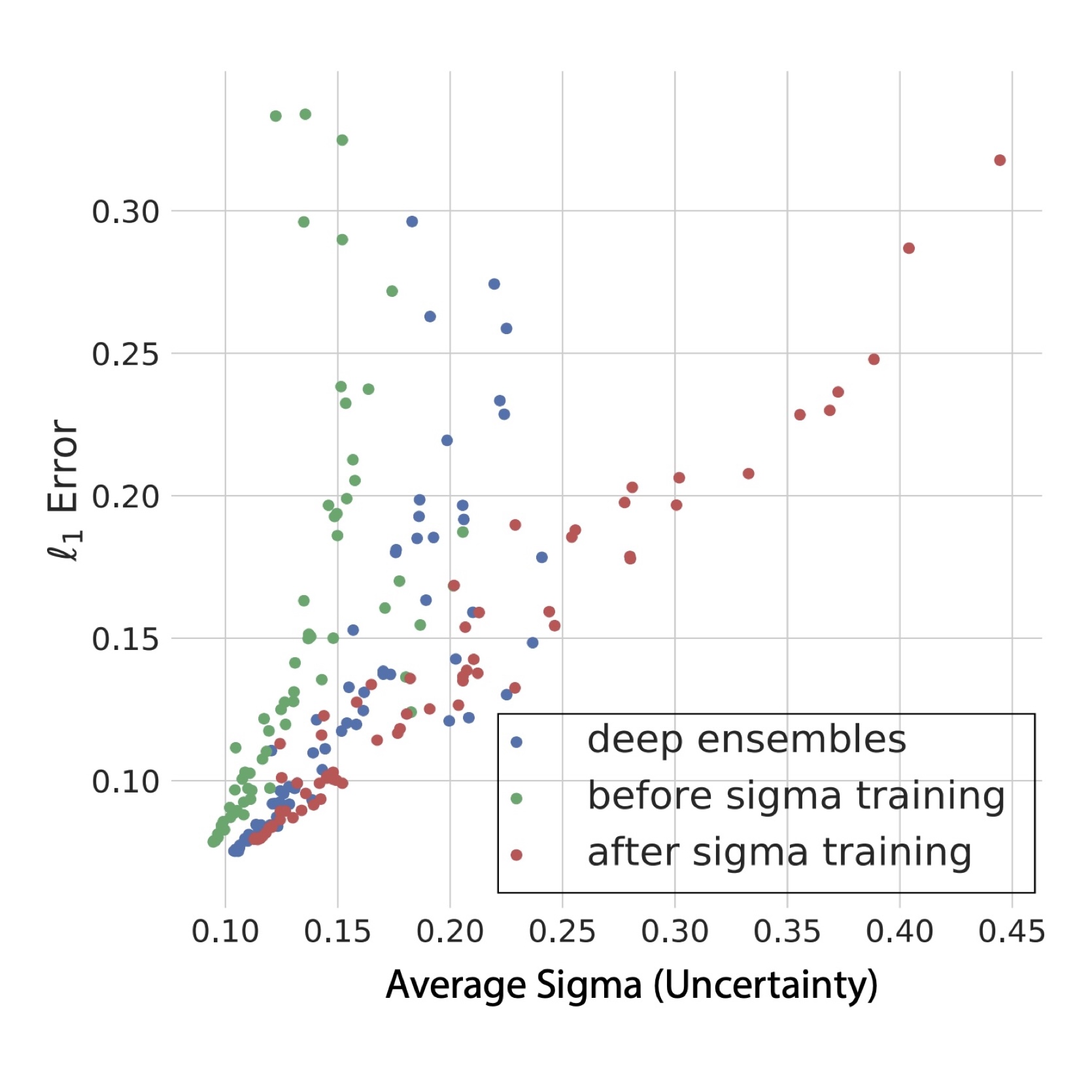
Robustness via Cross-Domain Ensembles
Oğuzhan Fatih Kar*, Teresa Yeo*, Alexander Sax, Amir Zamir ICCV, 2021 (Oral Presentation) project page / arXiv / github Joint uncertainty estimation for perception tasks. Calibration is supervised with a lightweight post-training step. |
|
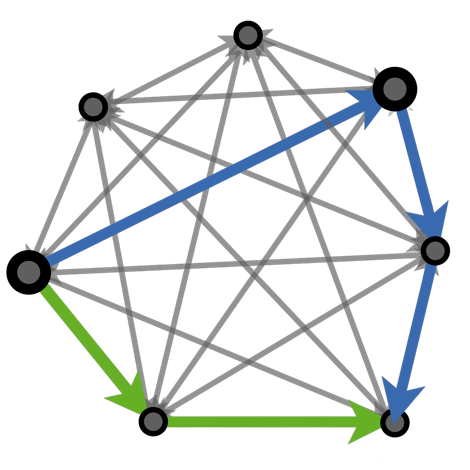
Robust Learning Through Cross-Task Consistency
Alexander Sax*, Amir Zamir*, Teresa Yeo, Oğuzhan Fatih Kar, Nikhil Cheerla, Rohan Suri, Zhangjie Cao, Jitendra Malik, Leonidas Guibas CVPR, 2020 (Best Paper Award Nominee) project page / arXiv / github Large-scale analysis of pretrained image-to-image networks. Compared to purely semantic perceptual losses like LPIPS, geometric perceptual consistency losses (depth/surface normal) yield sharper details and improve generalization to new domains. |
|
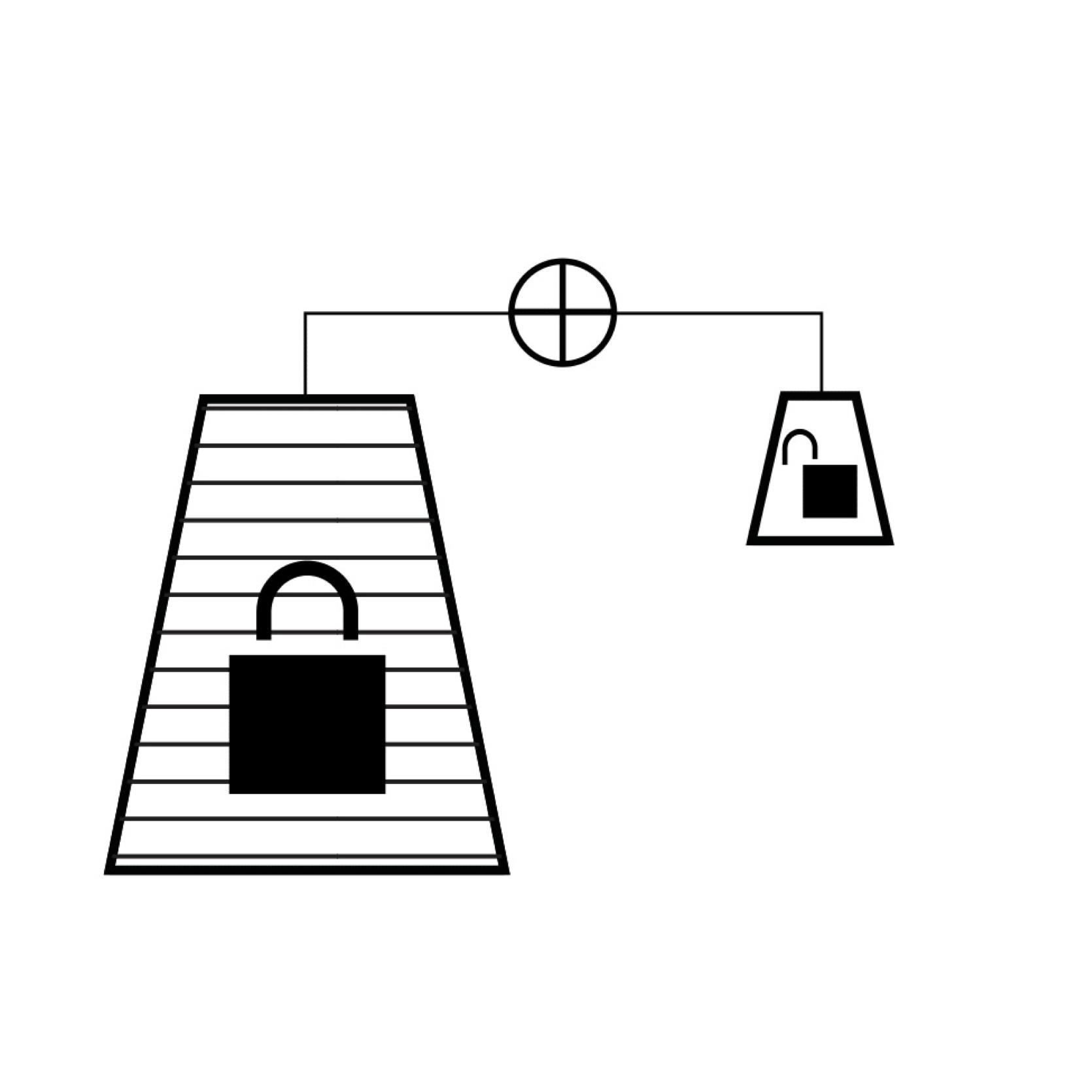
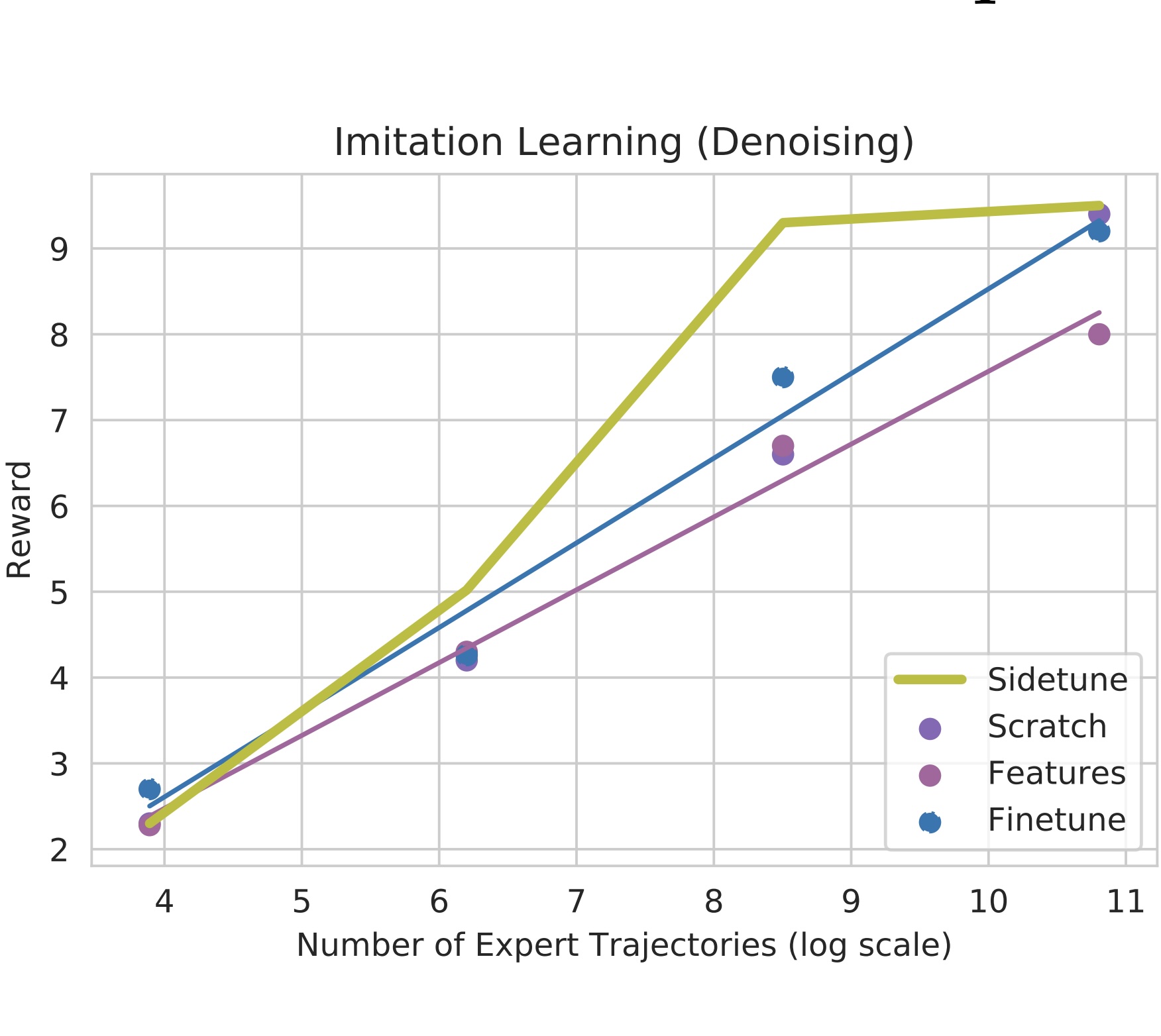
Side-Tuning: A Baseline for Network Adaptation via Additive Side Networks
Jeffrey O. Zhang, Alexander Sax, Amir Zamir, Leonidas Guibas, Jitendra Malik ECCV, 2020 (Spotlight) project page / arXiv / github Compared to full fine-tuning, and other parameter-efficient fine-tuning methods, simply adding a lightweight side network to control the activations is surprisingly competitive. We show results across vision, language, and robotics using both supervised learning and behavior cloning. |
|
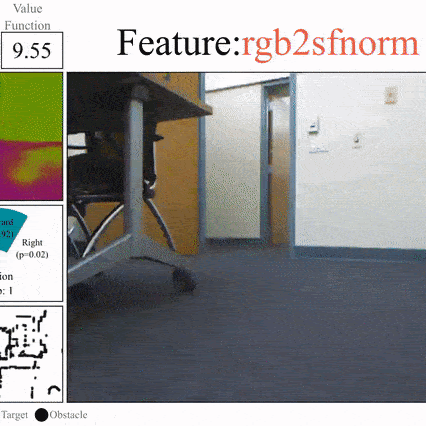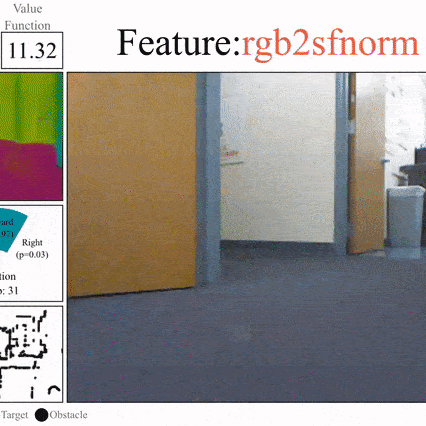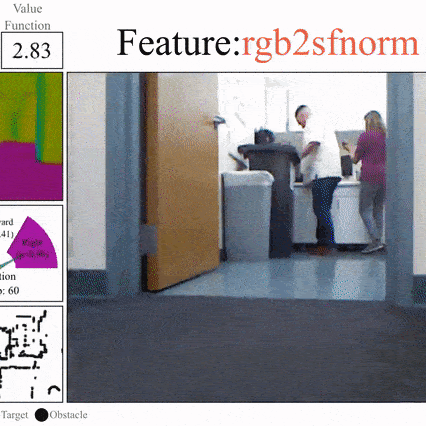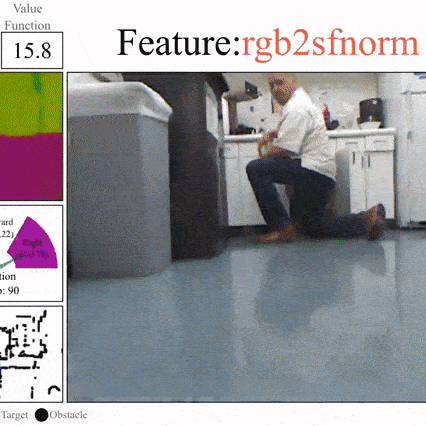
Robust Policies via Mid-Level Visual Representations: An Experimental Study in Manipulation and Navigation
Bryan Chen*, Alexander Sax*, Francis E. Lewis, Silvio Savarese, Jitendra Malik, Amir Zamir, Lerrel Pinto CoRL, 2020 project page / arXiv / github Pretrained visual representations enable faster learning and qualitatively better generalization compared to domain randomization, saturating the benchmark in settings where domain randomization fails entirely. Includes zero-shot sim-to-real on physical robots. We train policies with SAC and TD3 using hindsight experience replay (HER) for sample efficiency. |
|
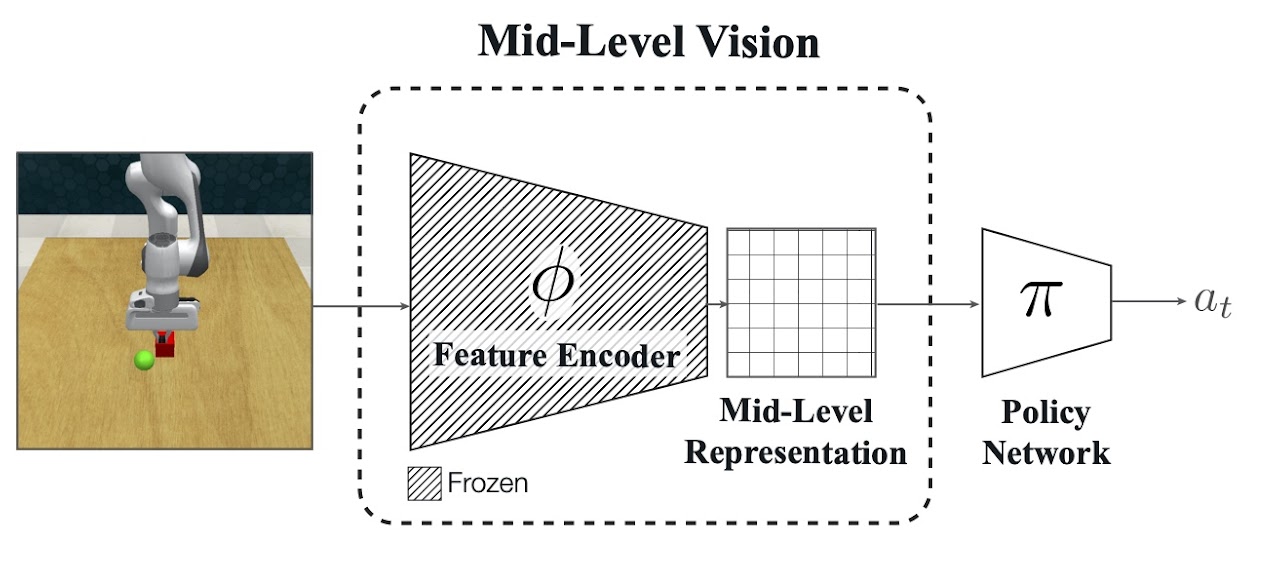
Learning to Navigate Using Mid-Level Visual Priors
Alexander Sax*, Jeffrey O. Zhang*, Bradley Emi, Amir Zamir, Leonidas Guibas, Silvio Savarese, Jitendra Malik CoRL, 2019 (Winner of CVPR19 Habitat Challenge RGB Track) project page / arXiv / github RL agents with pretrained image representations enable 10x sample efficiency gains vs. random init. We train navigation policies with PPO, adding importance sampling to enable off-policy learning with a replay buffer. |
|
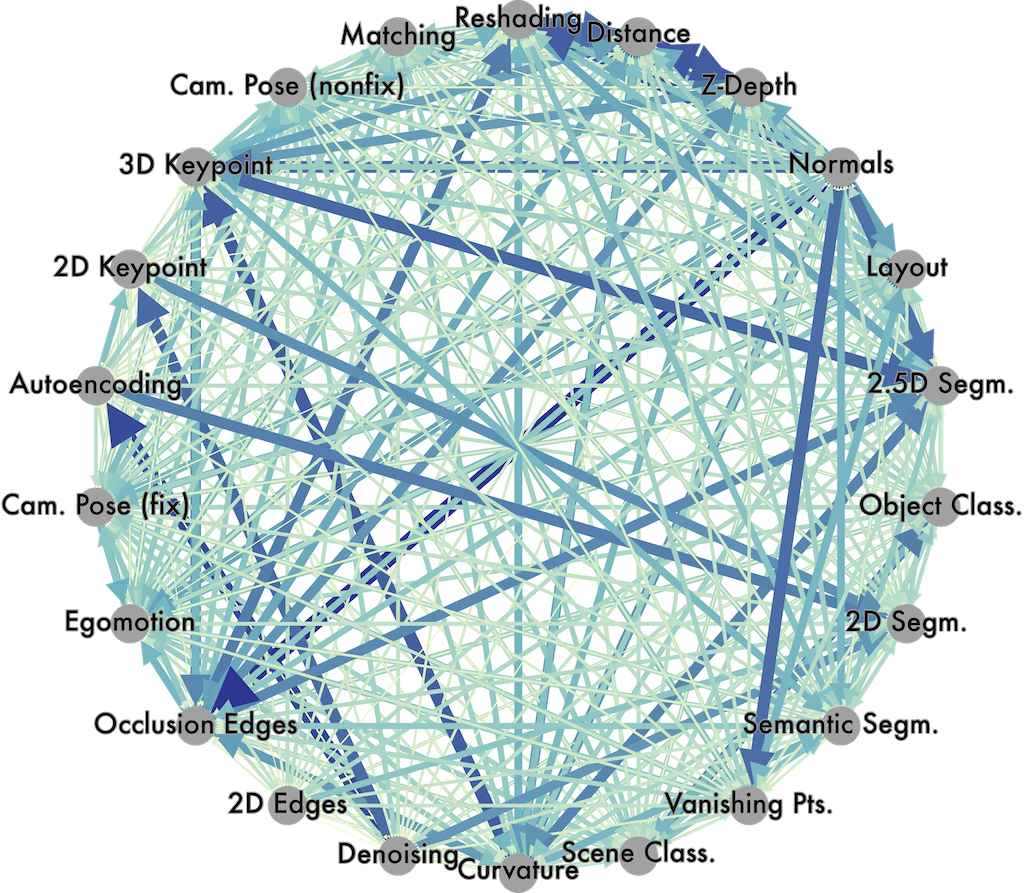
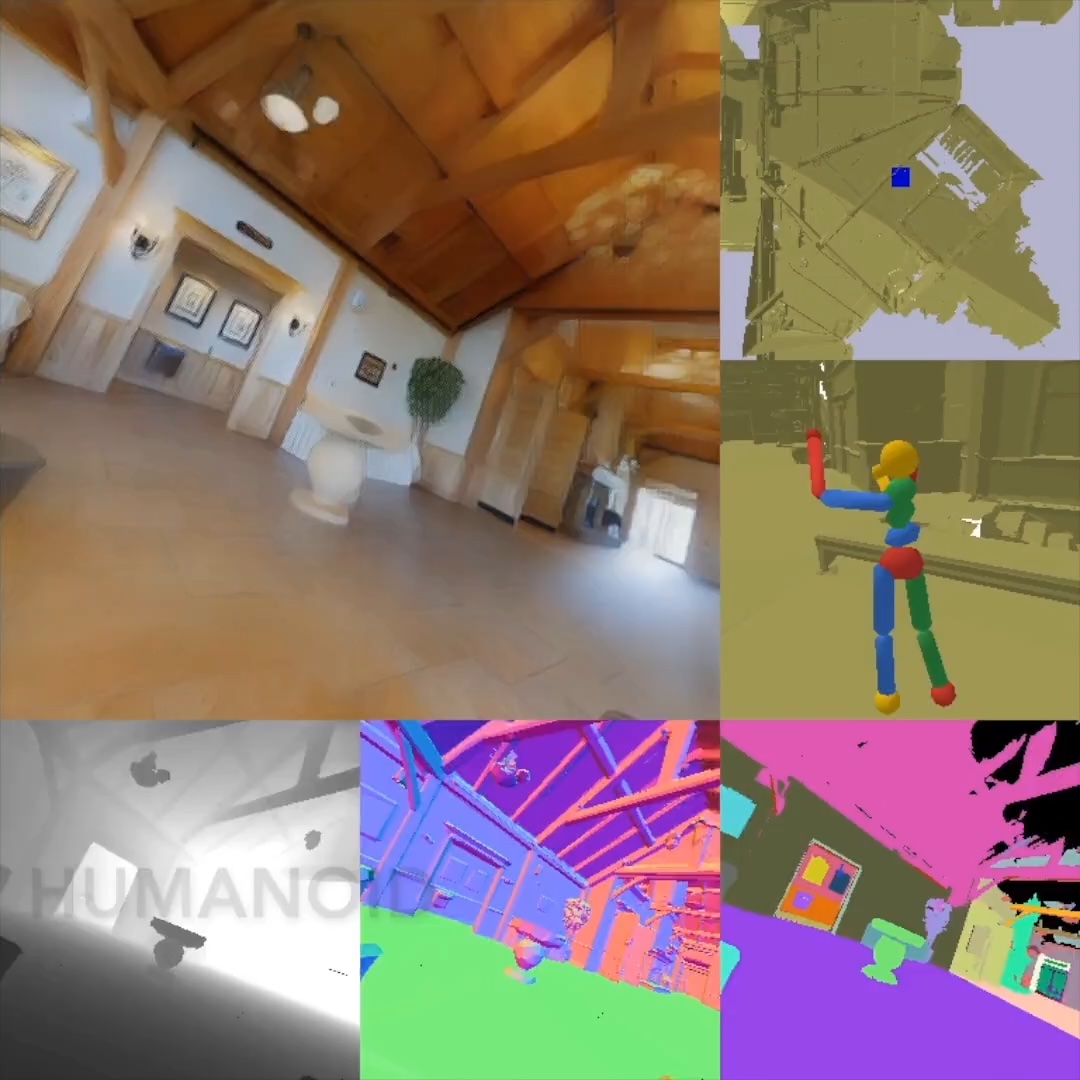
Taskonomy: Disentangling Task Transfer Learning
Amir Zamir, Alexander Sax*, William B. Shen*, Leonidas Guibas, Jitendra Malik, Silvio Savarese CVPR, 2018 (Best Paper Award) project page / arXiv / github A fully computational approach for modeling relationships across 26 fundamental vision tasks. Exploiting this structure with a pretraining/finetuning learning curriculum reduces overall supervision required by ~2/3. |

|
Gibson Env: Real-World Perception for Embodied Agents
Zhi-Yang He*, Fei Xia*, Amir Zamir*, Alexander Sax, Jitendra Malik, Silvio Savarese CVPR, 2018 (Spotlight, NVIDIA Pioneering Research Award) project page / arXiv / github A rendering and physics simulator to bridge the gap between large-scale simulation and real-world environments. The simulator features a database of thousands of real spaces and uses a generative model (GAN) for super-sampling. |
|
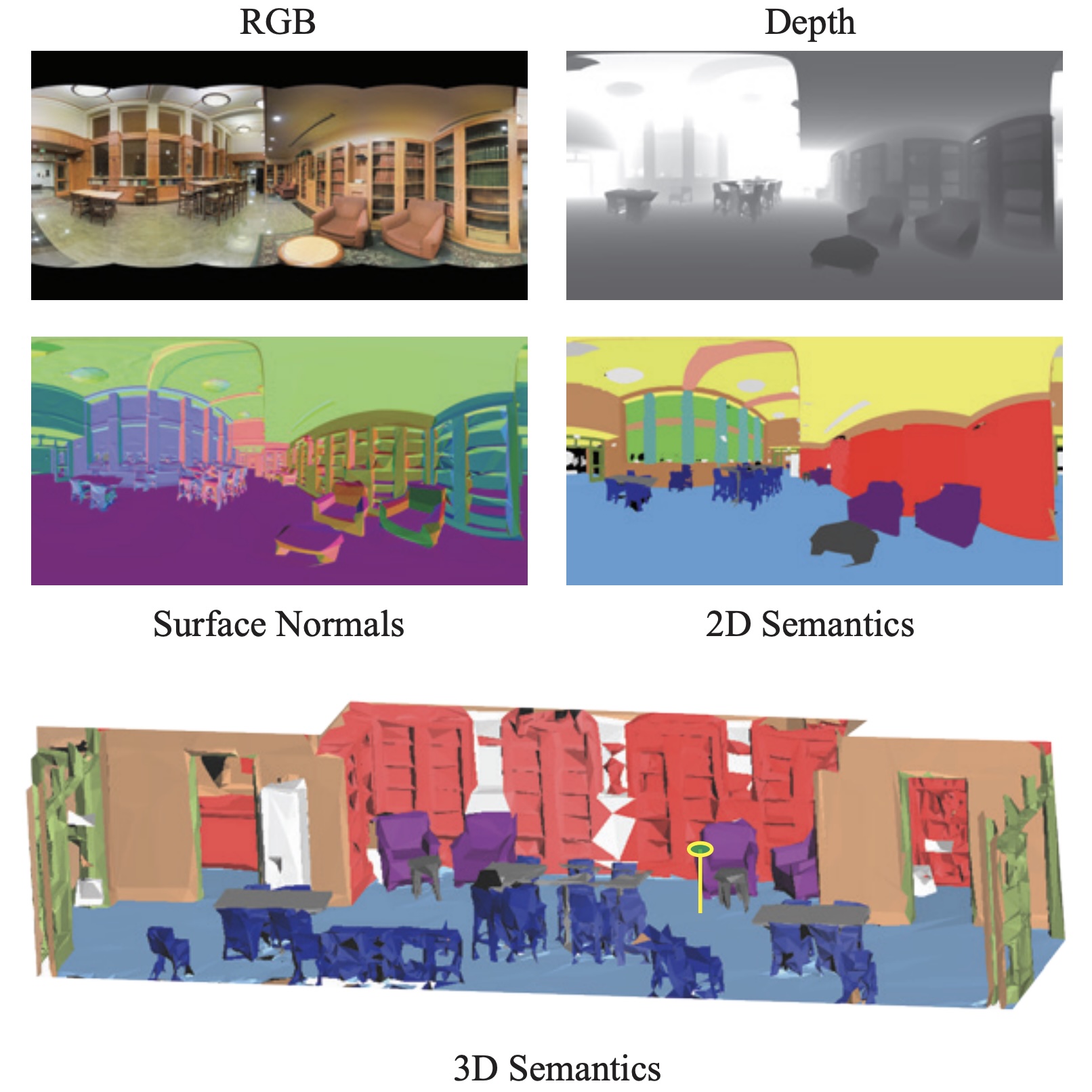
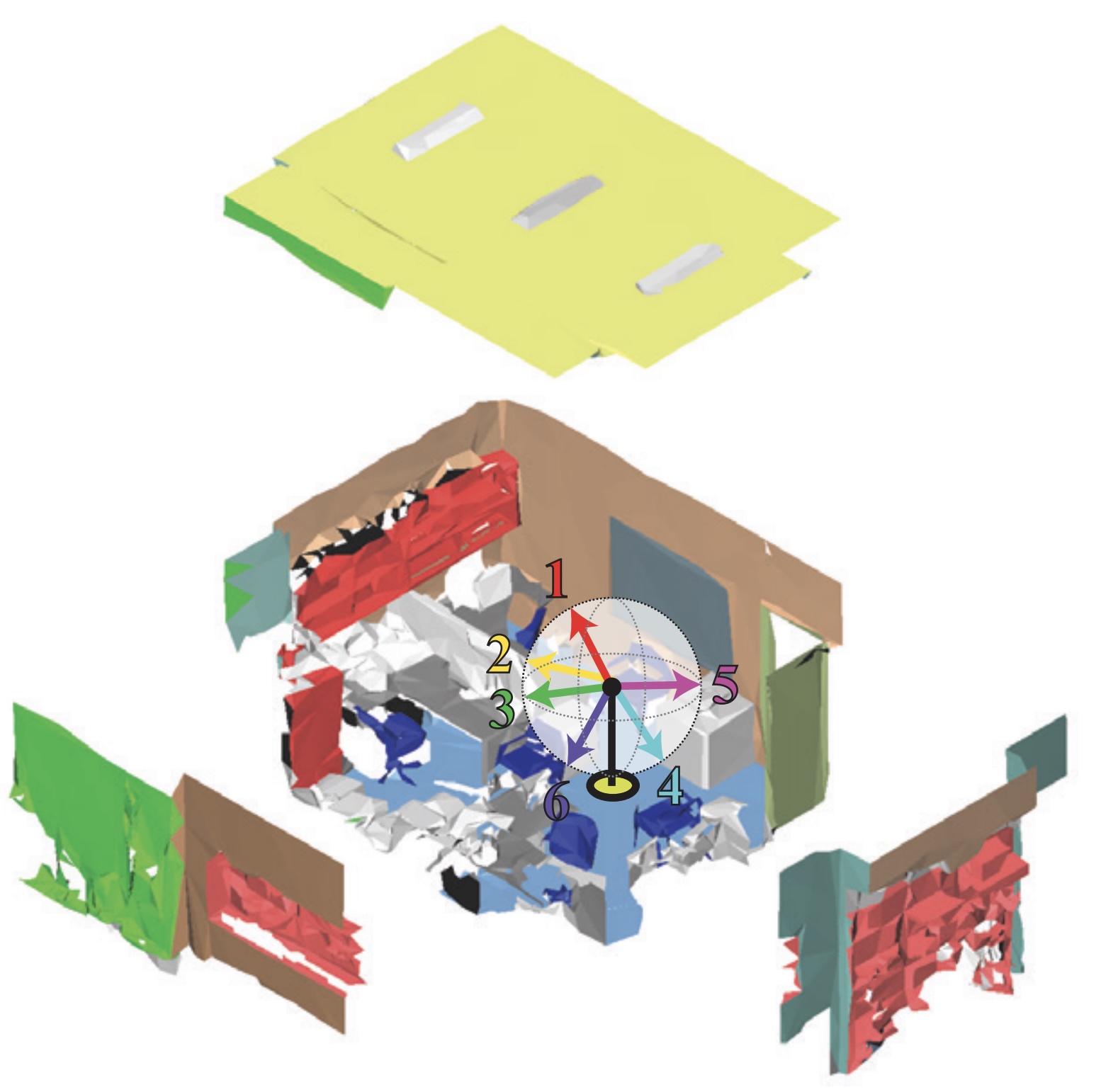
Joint 2D-3D-Semantic Data for Indoor Scene Understanding
Iro Armeni*, Alexander Sax*, Amir R. Zamir, Silvio Savarese arXiv, 2017 project page / arXiv / github A large-scale indoor dataset providing mutually registered 2D, 2.5D and 3D modalities with instance-level semantic annotations. Covers over 6,000m² across 6 large-scale indoor areas with 70,000+ RGB images and corresponding poses, depths, surface normals, semantic annotations, and pointmaps. |
Misc. |
|
Thanks Jon Barron for the clean website.
|